工厂模式
简单工厂
例如:设计一个消息发送功能模块,根据不同行为,创建不同的发送服务进行调用
1.创建接口
1
2
3
| public interface SendInterface {
void send(String receiver,String message);
}
|
2.创建接口实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class EmailService implements SendInterface{
@Override
public void send(String receiver, String message) {
System.out.println("发送给"+receiver+",信息:"+message);
}
}
public class InnerService implements SendInterface{
@Override
public void send(String receiver, String message) {
System.out.println("发送给"+receiver+",信息:"+message);
}
}
public class SmsService implements SendInterface{
@Override
public void send(String receiver, String message) {
System.out.println("发送给"+receiver+",信息:"+message);
}
}
|
3.使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class Notifacation {
public void send(String type,String receiver,String message){
SendInterface sendInterface = createSendInterfaceFactory(type);
sendInterface.send(receiver,message);
}
private SendInterface createSendInterfaceFactory(String type){
if("email".equals(type)){
return new EmailService();
}else if("sms".equals(type)){
return new SmsService();
}else if("inner".equals(type)){
return new InnerService();
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("发送类型错误");
}
}
}
|
简单工厂增强(增加缓存)
上面处理每次调用会创建新的对象,调用比较频繁会占用大量资源,可以创建后缓存起来,如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class Notifacation {
private static final Map<String,SendInterface> cacheMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
cacheMap.put("email",new EmailService());
cacheMap.put("sms",new SmsService());
cacheMap.put("inner",new InnerService());
}
public void send(String type,String receiver,String message){
SendInterface sendInterface = createSendInterface(type);
sendInterface.send(receiver,message);
}
private SendInterface createSendInterface(String type){
return cacheMap.get(type);
}
}
|
一般工厂
在简单工厂的基础上,进一步将创建实现类的行为剥离开
1.创建接口
1
2
3
| public interface SendInterfaceFactory {
SendInterface createSendInterface();
}
|
2.创建接口工厂
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class EmailServiceFactory implements SendInterfaceFactory{
@Override
public SendInterface createSendInterface() {
return new EmailService();
}
}
public class InnerServiceFactory implements SendInterfaceFactory{
@Override
public SendInterface createSendInterface() {
return new InnerService();
}
}
public class SmsServiceFactory implements SendInterfaceFactory{
@Override
public SendInterface createSendInterface() {
return new SmsService();
}
}
|
3.使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Notifacation {
private static final Map<String,SendInterfaceFactory> mapFactory = new HashMap<>();
static {
mapFactory.put("email",new EmailServiceFactory());
mapFactory.put("sms",new SmsServiceFactory());
mapFactory.put("inner",new InnerServiceFactory());
}
public void send(String type,String receiver,String message){
SendInterfaceFactory sendInterfaceFactory = createSendInterfaceFactory(type);
SendInterface sendInterface = sendInterfaceFactory.createSendInterface();
sendInterface.send(receiver,message);
}
private SendInterfaceFactory createSendInterfaceFactory(String type){
return mapFactory.get(type);
}
}
|
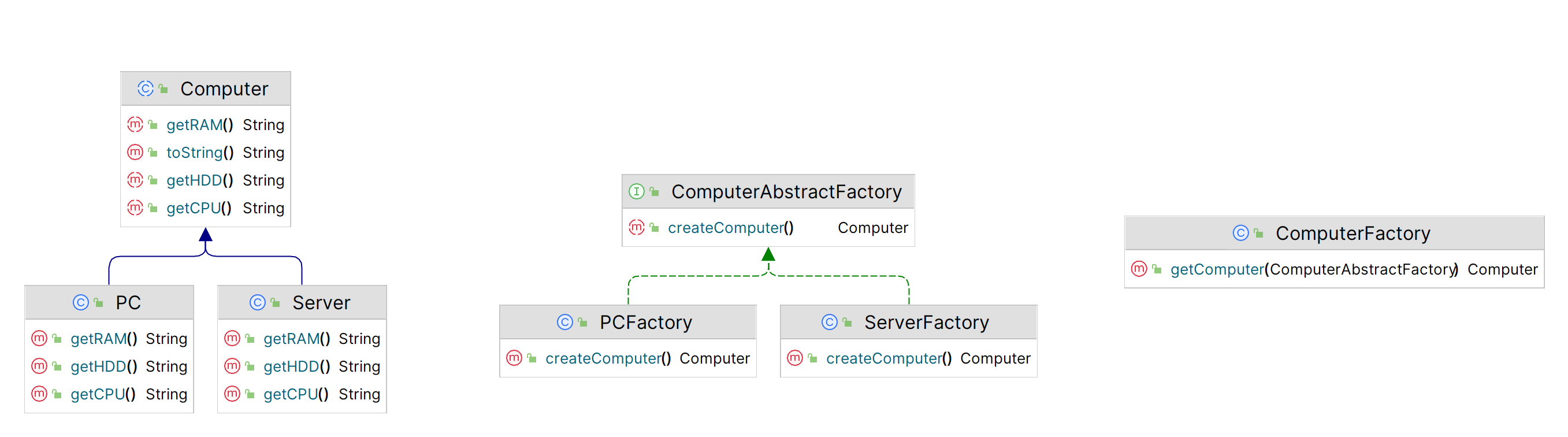
抽象工厂
根据输入的工厂返回子类
1.创建抽象类及子类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public abstract class Computer {
public abstract String getRAM();
public abstract String getHDD();
public abstract String getCPU();
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RAM = "+this.getRAM() +",HDD = "+this.getHDD() + ",CPU = "+this.getCPU();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class PC extends Computer{
private String ram;
private String hdd;
private String cpu;
public PC(String ram, String hdd, String cpu) {
this.ram = ram;
this.hdd = hdd;
this.cpu = cpu;
}
@Override
public String getRAM() {
return this.ram;
}
@Override
public String getHDD() {
return this.hdd;
}
@Override
public String getCPU() {
return this.cpu;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class Server extends Computer {
private String ram;
private String hdd;
private String cpu;
public Server(String ram, String hdd, String cpu){
this.ram=ram;
this.hdd=hdd;
this.cpu=cpu;
}
@Override
public String getRAM() {
return this.ram;
}
@Override
public String getHDD() {
return this.hdd;
}
@Override
public String getCPU() {
return this.cpu;
}
}
|
2.创建抽象工厂及子类
1
2
3
| public interface ComputerAbstractFactory {
Computer createComputer();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class PCFactory implements ComputerAbstractFactory {
private String ram;
private String hdd;
private String cpu;
public PCFactory(String ram, String hdd, String cpu) {
this.ram = ram;
this.hdd = hdd;
this.cpu = cpu;
}
@Override
public Computer createComputer() {
return new PC(ram,hdd,cpu);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class ServerFactory implements ComputerAbstractFactory {
private String ram;
private String hdd;
private String cpu;
public ServerFactory(String ram, String hdd, String cpu) {
this.ram = ram;
this.hdd = hdd;
this.cpu = cpu;
}
@Override
public Computer createComputer() {
return new Server(ram,hdd,cpu);
}
}
|
3.创建消费类
1
2
3
4
5
| public class ComputerFactory {
public static Computer getComputer(ComputerAbstractFactory computerAbstractFactory){
return computerAbstractFactory.createComputer();
}
}
|
4.使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class TestDesignPatterns {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testAbstractFactory();
}
private static void testAbstractFactory() {
Computer pc = ComputerFactory.getComputer(new PCFactory("2 GB","500 GB","2.4 GHz"));
Computer server = ComputerFactory.getComputer(new ServerFactory("16 GB","1 TB","2.9 GHz"));
System.out.println("AbstractFactory PC Config::"+pc);
System.out.println("AbstractFactory Server Config::"+server);
}
}
|
类图
![]()